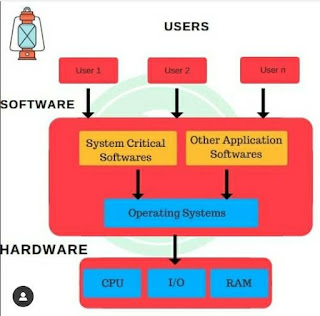
An operating system (OS) is the program that, after being initially loaded into the computer by a boot program, manages all of the other application programs in a computer. The application programs make use of the operating system by making requests for services through a defined application program interface (API). In addition, users can interact directly with the operating system through a user interface, such as a command-line interface (CLI) or a graphical UI (GUI).
Functions of an operating system
Although some operating systems offer unique features or designs, most have a consistent set of functions at their core:
- The user interface, either a graphical user interface (GUI) or a command-line interface (CLI), provides a way for users to interact with the operating system and perform operations outside of an application. The primary difference between these types of user interfaces is that a CLI uses a text-based terminal, whereas a GUI provides a visual desktop with icons and virtual buttons.
- The software platform is what gives application programs the foundation to operate. In most cases, an operating system launches and maintains the applications, facilitates the input to and output from the hardware, and manages the resources being used to run the application. These applications can also send requests for the operating system to perform specific tasks using an application program interface (API).
- The kernel provides base-level management of a device's underlying hardware. This includes the central processing unit (CPU), memory, USB ports, graphics devices, and storage devices.
Desktop operating systems
Most devices come with an operating system already preloaded. As such, the operating system a device has depends on the hardware manufacturer. A desktop or laptop computer will typically use one of the following operating systems:
- Microsoft Windows represents the largest share of operating systems in use today. Microsoft distributes Windows across its line of Surface devices and also licenses the software to almost all PC manufacturers—including Dell, HP, Lenovo, Asus, and Acer.
- macOS (formerly Mac OS X) is the operating system exclusive to Apple devices. Famous for its closed architecture designs, Apple developed macOS to run exclusively on its collection of Mac laptops and desktops.
- Linux is an open source operating system that's freely distributed for a number of hardware platforms. The Linux OS family was developed in the 1990s as a derivative of the commercial UNIX operating system.
Mobile operating systems
Most mobile devices, from smartphones to tablets to smartwatches, have dedicated operating systems that provide unique functionalities. Because these devices are usually smaller and offer limited resources, the operating systems prioritize efficiency and responsiveness. Popular developers for mobile device operating systems include:
- Apple, which has developed separate operating systems for each of its mobile devices: iOS for iPhone, iPadOS, and watchOS. Alongside macOS, each of these operating systems leverage iCloud to create a seamless user experience across devices.
- Microsoft, which included support for tablets in its 2015 release of Windows 10.
- Google, whose Android operating system dominates the market for tablets and smartphones. Amazon's line of Fire tablets use an adapted version of the Android software, called Fire OS, that maintains most of the core features but has a heavier focus on Amazon services like Prime Video, Amazon Music, Kindle, and Audible.
Real-time operating systems
Some operating systems are embedded in devices that serve a niche purpose, like medical devices, automated teller machines (ATMs), and smart home devices. These operating systems are called real-time operating systems (RTOS) because they perform actions within a set amount of time and process data as soon as it's received. An RTOS is generally much lighter than a mobile or desktop operating system, so it's developed to execute a limited number of operations with high efficiency and reliability.








Thanks sir
ReplyDeleteThanks sir
ReplyDelete